The aim of this post is to summarize:
- What’s required for collisions in Unity
- How to setup some basic collision detection
- When
OnTriggerandOnCollisionare called and when they aren’t
What’s required for collision to occur?
For collisions to be detected by Unity, there are 2 components that are of particular importance:
1. Rigidbody
- Allows an object to react to physics
- A key property to note is:
isKinematic - If you do not require the object to have physics-based interactions with other objects (i.e.
isKinematicistrue), aRigidbodyis still required (on at least 1 object) for any collision to occur
2. Collider
- Used to define the shape of the object (or rather an approximation of it) which will be used for collisions
- There are various types of colliders, namely; Box, Sphere, Capsule, Mesh, etc
- A key property to note is:
isTrigger
How to setup basic collision detection?
1. When you need two solid objects to interact with each other:
- Object 1:
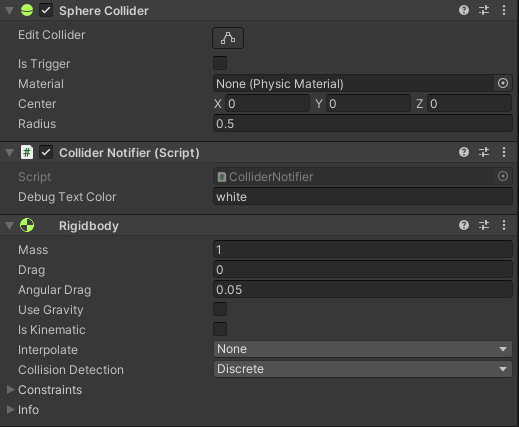
- Object 2:

Notes:
- At least one
Rigidbodyneeds to be non-kinematic (i.e.isKinematic = false)
Callbacks that will be called:
OnCollisionEnterOnCollisionExit

2. When you want to do something when a collision occurs (i.e. a trigger) on a non-physical object.
- Object 1:
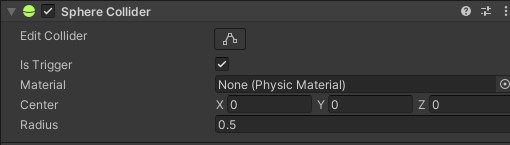
- Object 2:
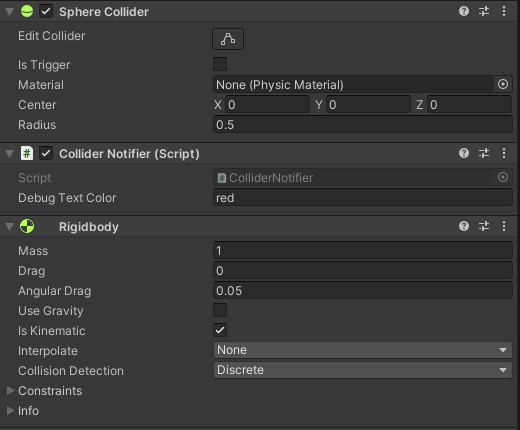
Notes:
- At least one object requires a
RigidbodyisKinematiccan be eithertrueorfalse
- At least 1
Colliderneeds to haveisTrigger = true- Both cannot be set to
isTrigger = true
- Both cannot be set to
Callbacks that will be called:
OnTriggerEnterOnTriggerExit